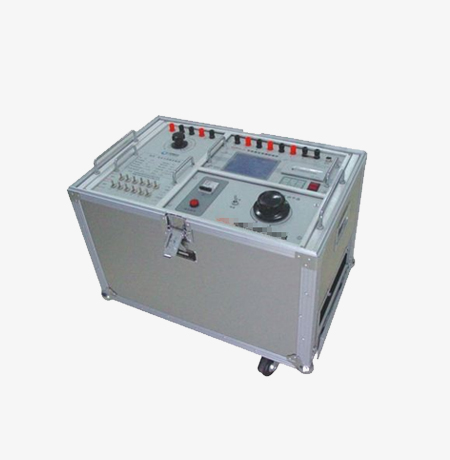
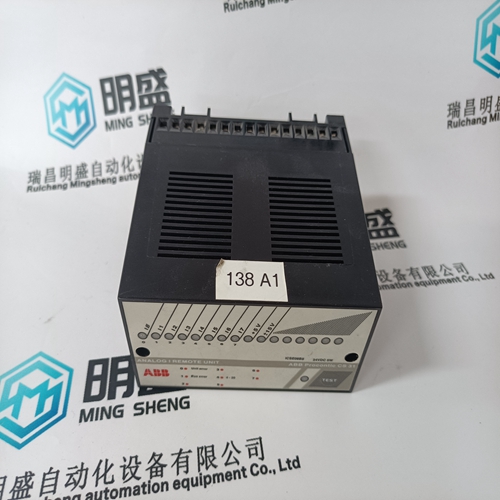
Home > Product > DCS control system > YOKOGAWA 16147-51-02 output module
YOKOGAWA 16147-51-02 output module
- Product ID: 16147-51-02
- Brand: YOKOGAWA
- Place of origin: JAPAN
- Goods status: new/used
- Delivery date: stock
- The quality assurance period: 365 days
- Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:+86 15270269218
- Email:xiamen2018@foxmail.com
- Tags:YOKOGAWA16147-51-02output module
- Get the latest price:Click to consult
YOKOGAWA 16147-51-02 output module
Connect Hall Sensors if available.
Hall sensors are only used with sinusoidal commutation and are not necessary for proper
operation. The use of hall sensors allows the controller to automatically estimate the
commutation phase upon reset and also provides the controller the ability to set a more precise
commutation phase. Without hall sensors, the commutation phase must be determined
manually.
The hall effect sensors are connected to the digital inputs of the controller. These inputs can
be used with the general use inputs (bits 1-8), the auxiliary encoder inputs (bits 81-96), or the
extended I/O inputs of the DMC-21x3 controller (bits 17-56).
NOTE: The general use inputs are TTL - for more information regarding the digital inputs, see
Chapter 3, Connecting Hardware.
Each set of sensors must use inputs that are in consecutive order.
Connect Standard Servo Motors
The following discussion applies to connecting the DMC-21x3 controller to standard servo motor amplifiers: If the user is working with the Galil AMP-20340 or AMP-20440, then simply wire the motor leads and encoder signals as shown in the appendix. The motor and the amplifier may be configured in the torque or the velocity mode. In the torque mode, the amplifier gain should be such that a 10 Volt signal generates the maximum required current. In the velocity mode, a command signal of 10 Volts should run the motor at the maximum required speed. Step by step directions on servo system setup are also included on the WSDK (Windows Servo Design Kit) software offered by Galil. See section on WSDK for more details. Step A. Check the Polarity of the Feedback Loop It is assumed that the motor and amplifier are connected together and that the encoder is operating correctly (Step B). Before connecting the motor amplifiers to the controller, read the following discussion on setting Error Limits and Torque Limits. Note that this discussion only uses the A axis as an example.
Set the Error Limit as a Safety Precaution
Usually, there is uncertainty about the correct polarity of the feedback. The wrong polarity
causes the motor to run away from the starting position. Using a terminal program, such as
Galil SmartTerminal, the following parameters can be given to avoid system damage:
Input the commands:
ER 2000