Home > Product > Gas turbine system > GE DS200IPCSG2A Interface components
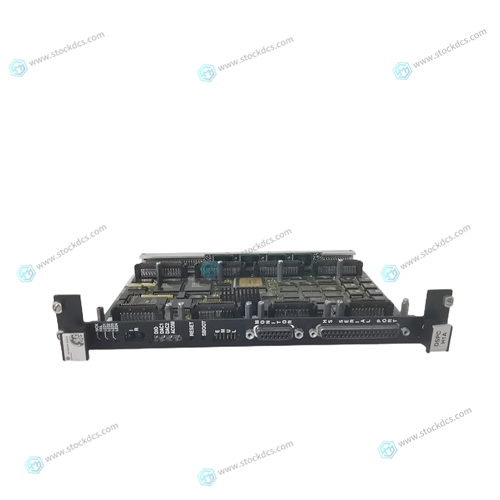
GE DS200IPCSG2A Interface components
- Product ID: DS200IPCSG2A
- Brand: GE
- Place of origin: The United States
- Goods status: new/used
- Delivery date: stock
- The quality assurance period: 365 days
- Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:+86 15270269218
- Email:stodcdcs@gmail.com
- Tags:GEDS200IPCSG2AInterface components
- Get the latest price:Click to consult
GE DS200IPCSG2A Interface components
Technically R is an expression language with a very simple syntax. It is case sensitive as are most UNIX based packages, so A and a are different symbols and would refer to different variables. The set of symbols which can be used in R names depends on the operating system and country within which R is being run (technically on the locale in use). Normally all alphanumeric symbols are allowed1 (and in some countries this includes accented letters) plus ‘.’ and ‘_’, with the restriction that a name must start with ‘.’ or a letter, and if it starts with ‘.’ the second character must not be a digit. Names are effectively unlimited in length. Elementary commands consist of either expressions or assignments. If an expression is given as a command, it is evaluated, printed (unless specifically made invisible), and the value is lost. An assignment also evaluates an expression and passes the value to a variable but the result is not automatically printed.
Recall and correction of previous commands
Under many versions of UNIX and on Windows, R provides a mechanism for recalling and reexecuting previous commands. The vertical arrow keys on the keyboard can be used to scroll forward and backward through a command history. Once a command is located in this way, the cursor can be moved within the command using the horizontal arrow keys, and characters can be removed with the DEL key or added with the other keys. More details are provided later: see Appendix C [The command-line editor], page 92. The recall and editing capabilities under UNIX are highly customizable. You can find out how to do this by reading the manual entry for the readline library. Alternatively, the Emacs text editor provides more general support mechanisms (via ESS, Emacs Speaks Statistics) for working interactively with R. See Section “R and Emacs” in The R statistical system FAQ.
Data permanency and removing objects
The entities that R creates and manipulates are known as objects. These may be variables, arrays of numbers, character strings, functions, or more general structures built from such components. During an R session, objects are created and stored by name (we discuss this process in the next section). The R command > objects() (alternatively, ls()) can be used to display the names of (most of) the objects which are currently stored within R. The collection of objects currently stored is called the workspace.







Company product range
----------------------Ruichang Mingsheng Automation Equipment Co., Ltd----------------------
PLC module, programmable controller, CPU module, IO module, DO module, AI module, DI module
Network communication module,
Ethernet module, motion control module, analog input module, analog output module, digital input module, digital output
Module, redundancy module, power module, relay output module, relay input module, processor module