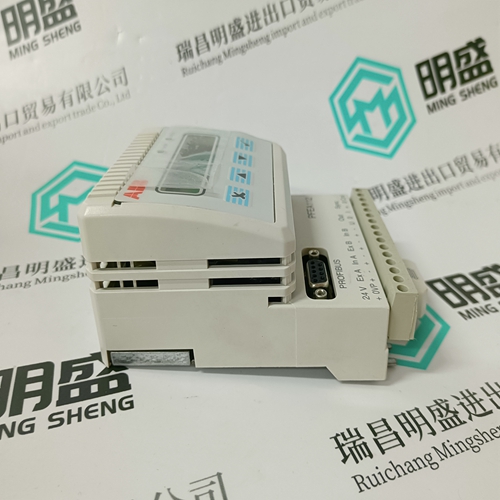
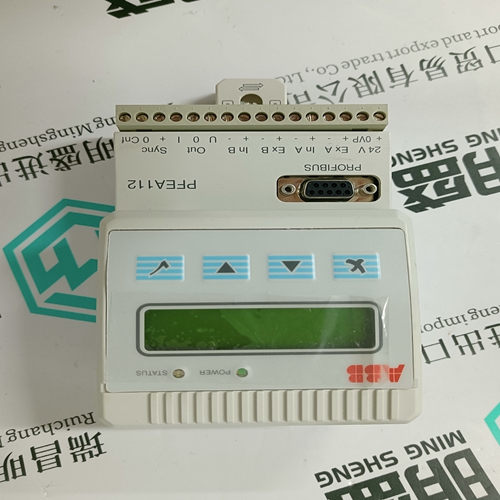
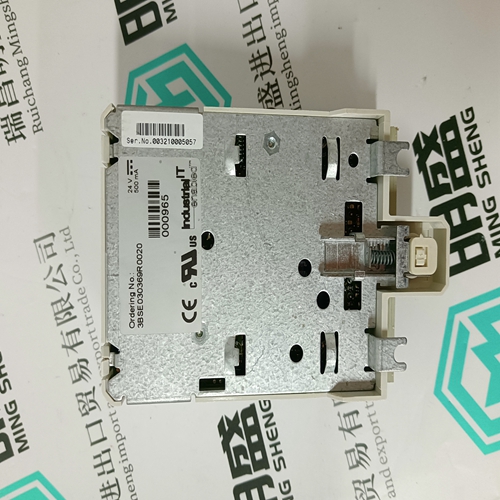
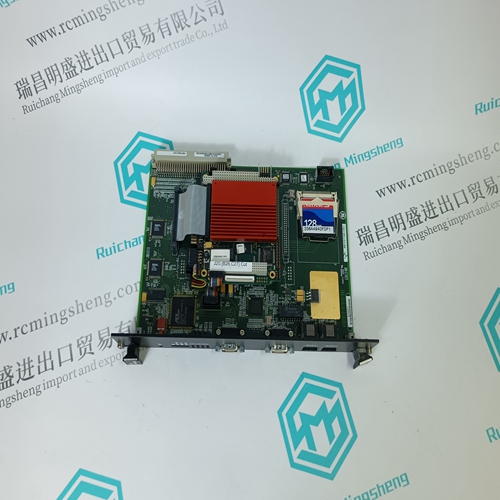
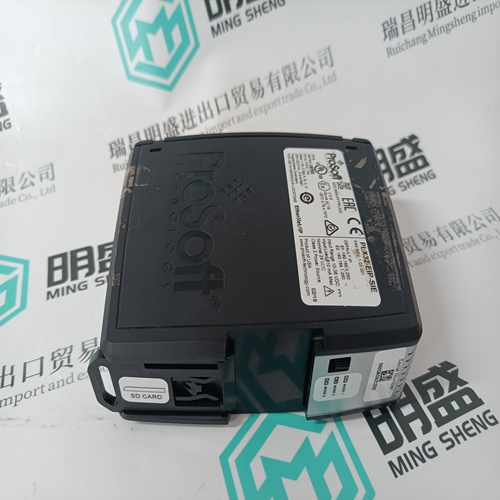
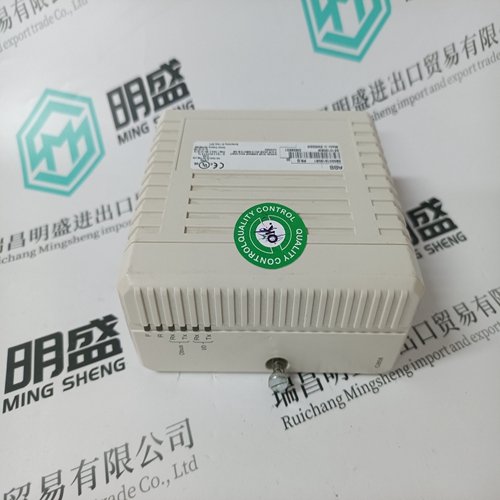
Home > Product > DCS control system > PFEA112-20 3BSE030369R0020 Tension controller
PFEA112-20 3BSE030369R0020 Tension controller
- Product ID: PFEA112-20 3BSE030369R0020
- Brand: ABB
- Place of origin: The Swiss
- Goods status: new/used
- Delivery date: stock
- The quality assurance period: 365 days
- Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:+86 15270269218
- Email:stodcdcs@gmail.com
- Tags:PFEA112-20 3BSE030369R0020Tension controller
- Get the latest price:Click to consult
The main products
Spare parts spare parts, the DCS control system of PLC system and the robot system spare parts,
Brand advantage: Allen Bradley, BentlyNevada, ABB, Emerson Ovation, Honeywell DCS, Rockwell ICS Triplex, FOXBORO, Schneider PLC, GE Fanuc, Motorola, HIMA, TRICONEX, Prosoft etc. Various kinds of imported industrial parts
PFEA112-20 3BSE030369R0020 Tension controller
Data Frame Format and Data Rate One data frame of an asynchronous transmission to or from a PQMII consists of 1 start bit, 8 data bits, and 1 stop bit, resulting in a 10-bit data frame. This is important for high-speed modem transmission, since 11-bit data frames are not supported by Hayes modems at bit rates greater than 300 bps. The Modbus protocol can be implemented at any standard communication speed. The PQMII supports operation at 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, and 19200 baud. 7.1.4 Data Packet Format A complete request/response sequence consists of the following bytes (transmitted as separate data frames): Master Request Transmission: SLAVE ADDRESS: 1 byte FUNCTION CODE: 1 byte DATA: variable number of bytes depending on the Function Code CRC: 2 bytes Slave Response Transmission: SLAVE ADDRESS: 1 byte FUNCTION CODE: 1 byte DATA: variable number of bytes depending on FUNCTION CODE CRC: 2 bytes The Slave Address is the first byte of every transmission. It represents the user-assigned address of the slave device assigned to receive the message sent by the master. Each slave device must be assigned a unique address so only it responds to a transmission that starts with its address. In a master request transmission, the Slave Address represents the address to which the request is being sent. In a slave response transmission the Slave Address represents the address sending the response.
A master transmission
with a Slave Address of 0 indicates a broadcast command. Broadcast commands can be used only to store setpoints or perform commands. The Function Code is the second byte of every transmission. Modbus defines function codes of 1 to 127. The PQMII implements some of these functions. See 7.2.1 Supported Modbus Functions for details of the supported function codes. In a master request transmission the Function Code tells the slave what action to perform. In a slave response transmission if the Function Code sent from the slave is the same as the Function Code sent from the master then the slave performed the function as requested. If the high order bit of the Function Code sent from the slave is a 1 (i.e. if the Function Code is > 127) then the slave did not perform the function as requested and is sending an error or exception response. The Data is a variable number of bytes depending on the Function Code. This may be Actual Values, Setpoints, or addresses sent by the master to the slave or by the slave to the master. See 7.2.1 Supported Modbus Functions for a description of the supported functions and the data required for each. The CRC is a a two byte error checking code. See the following section for details.