Home > Product > DCS control system > FCP280 RH924YA control module
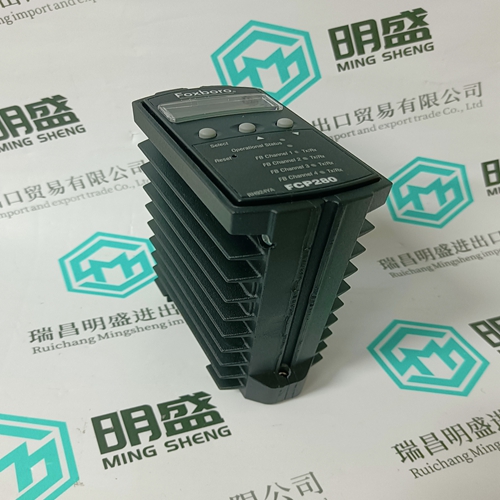
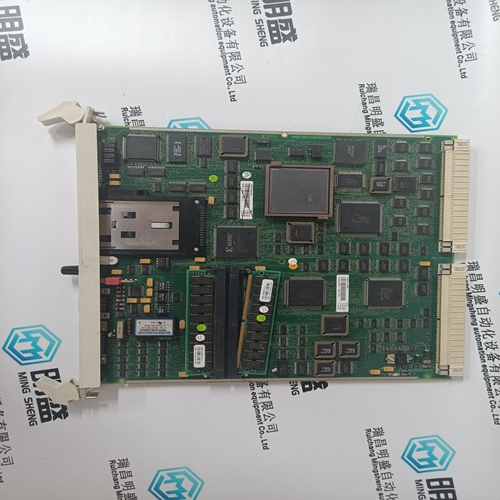
FCP280 RH924YA control module
- Product ID: FCP280 RH924YA
- Brand: FOXBORO
- Place of origin: The United States
- Goods status: new/used
- Delivery date: stock
- The quality assurance period: 365 days
- Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:+86 15270269218
- Email:stodcdcs@gmail.com
- Tags:FCP280 RH924YAcontrol module
- Get the latest price:Click to consult
The main products
Spare parts spare parts, the DCS control system of PLC system and the robot system spare parts,
Brand advantage: Allen Bradley, BentlyNevada, ABB, Emerson Ovation, Honeywell DCS, Rockwell ICS Triplex, FOXBORO, Schneider PLC, GE Fanuc, Motorola, HIMA, TRICONEX, Prosoft etc. Various kinds of imported industrial parts
FCP280 RH924YA control module
The RTU version of Modbus includes a 2-byte CRC-16 (16-bit cyclic redundancy check) with every transmission. The CRC-16 algorithm essentially treats the entire data stream (data bits only; start, stop and parity are ignored) as one continuous binary number. This number is first shifted left 16 bits and then divided by a characteristic polynomial (11000000000000101B). The 16-bit remainder is appended to the end of the transmission, MSByte first. The resulting message including CRC, when divided by the same polynomial at the receiver, results in a zero remainder if no transmission errors have occurred. If a PQMII Modbus slave device receives a transmission in which an error is indicated by the CRC-16 calculation, the slave device will not respond to the transmission. A CRC-16 error indicates that one or more bytes of the transmission were received incorrectly and thus the entire transmission should be ignored in order to avoid the PQMII performing any incorrect operation. The CRC-16 calculation is an industry standard method used for error detection. An algorithm is included here to assist programmers in situations where no standard CRC-16 calculation routines are available.
CRC-16 Algorithm
Once the following algorithm is complete, the working register “A” will contain the CRC value to be transmitted. Note that this algorithm requires the characteristic polynomial to be reverse bit ordered. The MSbit of the characteristic polynomial is dropped since it does not affect the value of the remainder. The following symbols are used in the algorithm: -->: data transfer; A: 16-bit working register; AL: low order byte of A; AH: high order byte of A; CRC: 16-bit CRC-16 value; i and j: loop counters; (+): logical exclusive-OR operator; Di: i-th data byte (i = 0 to N – 1); G: 16-bit characteristic polynomial = 1010000000000001 with MSbit dropped and bit order reversed; shr(x): shift right (the LSbit of the low order byte of x shifts into a carry flag, a '0' is shifted into the MSbit of the high order byte of x, all other bits shift right one location Data packet synchronization is maintained by timing constraints. The receiving device must measure the time between the reception of characters. If three and one half character times elapse without a new character or completion of the packet, then the communication link must be reset (i.e. all slaves start listening for a new transmission from the master). Thus at 9600 baud a delay of greater than 3.5 × 1/9600 × 10 = 3.65 ms will cause the communication link to be reset.