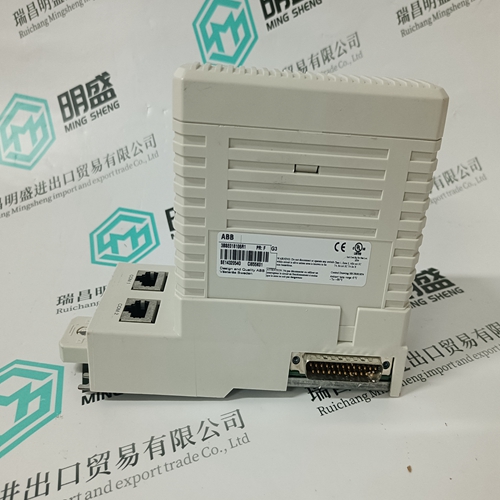
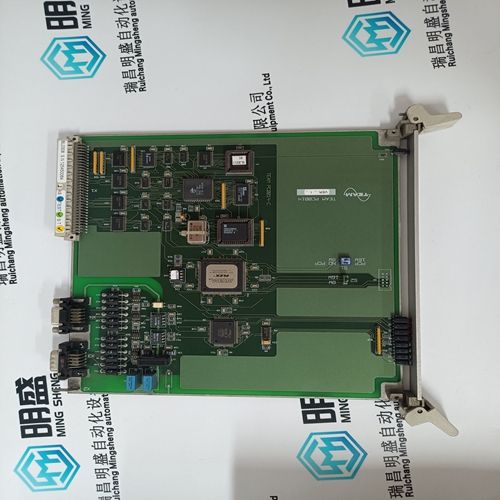
Home > Product > DCS control system > PM891 3BSE053240R1 conversion module
PM891 3BSE053240R1 conversion module
- Product ID: PM891 3BSE053240R1
- Brand: ABB
- Place of origin: The Swiss
- Goods status: new/used
- Delivery date: stock
- The quality assurance period: 365 days
- Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:+86 15270269218
- Email:stodcdcs@gmail.com
- Tags:PM891 3BSE053240R1conversion module
- Get the latest price:Click to consult
The main products
Spare parts spare parts, the DCS control system of PLC system and the robot system spare parts,
Brand advantage: Allen Bradley, BentlyNevada, ABB, Emerson Ovation, Honeywell DCS, Rockwell ICS Triplex, FOXBORO, Schneider PLC, GE Fanuc, Motorola, HIMA, TRICONEX, Prosoft etc. Various kinds of imported industrial parts
PM891 3BSE053240R1 conversion module
Blocks 0 and 1 are reserved for Data Logger Data Interval information. Block 2 contains header information for both Data Logs. The first 32 registers of Block 2 are reserved for Data Log 1 header information, and the remaining 32 registers are reserved for Data Log 2 header information. The first register of Data Log information resides at Register 0 of Block 3. This leaves 196224 bytes of data storage.The location of the first Record in Log 2 will depend upon the Log configuration. Its location is determined by reading the Log 2 Header value for Log Start Address at location 0AB2 and 0AB3 in the memory map. The Log Start Address consists of the block number (0AB2) and the register number (0AB3) which represents the location of the first record within the Data Log memory structure. This location will always be the starting address for Data Log 2 for the given configuration. Adding or deleting parameters to the configuration will change the Log 2 Starting Address. The log pointers contain a value from 0 to 196607 representing a byte within the data Log memory structure. Add 1 to this number and then divide this number by 64 (number of registers in a Block). Then divide this number by 2 (number of bytes in a register), and truncate the remainder of the division to determine the Block number. Multiplying the remainder of the division by 64 will determine the Register number. For example, if the Log pointer: “Log 2 Pointer to First Item of First Record” was 34235, then the Block and Register numbers containing the first record of Log 2 are: Block Number = (34235 + 1) / 64 / 2 = 267.46875 Therefore, Block Number 267 contains the starting record. Record Number = 0.46875 × 64 = 30
Accessing Data Log Information
The Data Log can be accessed using the EnerVista PQMII Setup Software or manually via the serial port. Access via the EnerVista PQMII Setup Software is described in Data Logger on page 4–12. Access manually via the serial port as follows: 1. Set the Block of data you wish to access at 1268h in the PQMII Memory Map. 2. Read the required amount of data from the 64 Registers in the Block. Accessing the Data Log in this manner assumes that the user knows which Block they wish to access, and knows the size of each Record based upon the parameters they have selected to log. The easiest way to access the data in the Data Log is to read the entire log and export this data into a spreadsheet for analysis. This requires defining the Block to be read, starting at Block 0, and reading all 128 bytes of data in each of the 64 Registers within the Block. You would then define Blocks 1, 2, 3, etc., and repeat the reading of the 64 Registers for each block, until Block 1535. This requires 1536 reads of 128 bytes each. The data can then be interpreted based upon the parameter configuration.