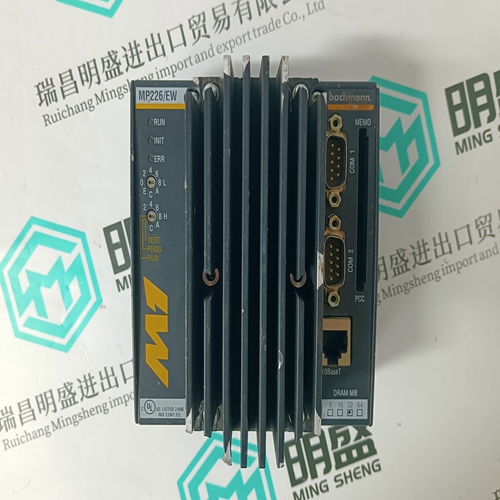
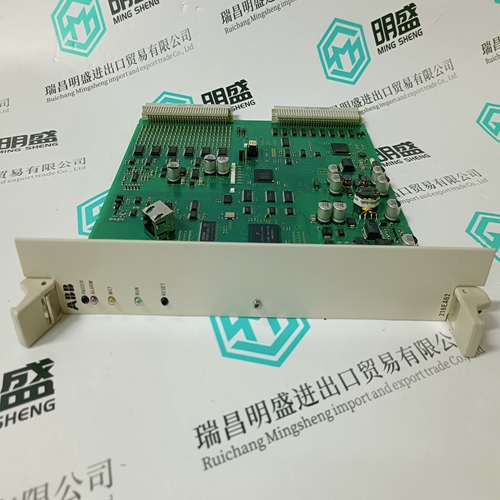
Home > Product > DCS control system > ABB CMA121 3DDE300401 Data acquisition card
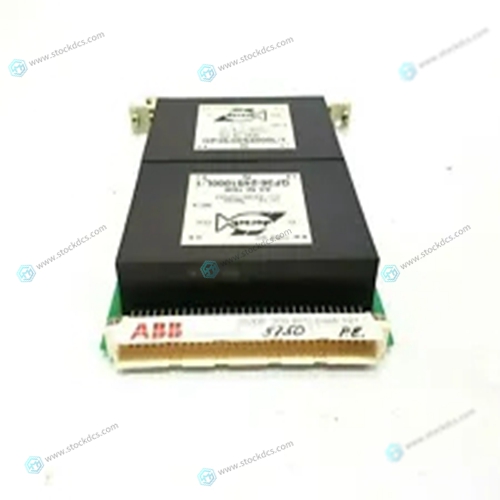
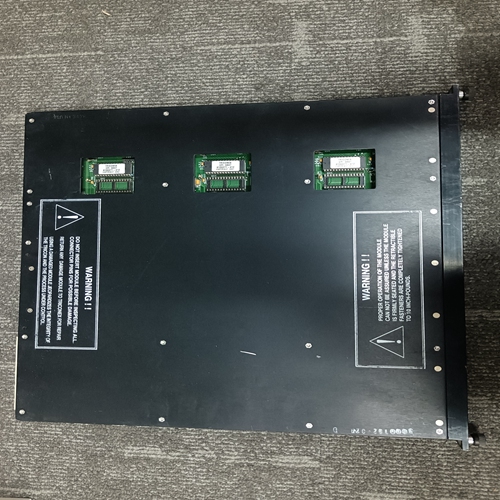
ABB CMA121 3DDE300401 Data acquisition card
- Product ID: CMA121 3DDE300401
- Brand: ABB
- Place of origin: The Swiss
- Goods status: new/used
- Delivery date: stock
- The quality assurance period: 365 days
- Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:+86 15270269218
- Email:stodcdcs@gmail.com
- Tags:ABBCMA1213DDE300401Data acquisition card
- Get the latest price:Click to consult
ABB CMA121 3DDE300401 Data acquisition card
The following illustration shows the RadioLinx Industrial Hotspot Browser (page 123) application provided with the radios. Notice it shows the radio named Hematite_4F, linked to Amethyst_BD. This link is shown with a red dotted line. Also visible is the level of redundancy in their network. Each of the blue lines represents an alternate parent. From this view, it is easily shown how much redundancy exists in their network.To display the redundant paths, select the toolbar button denoting two "parents." To view the redundancy on a per-radio basis, select the single "parent" button, and then click on the radio to view its available redundancies.Note: Different versions of the RLX2 Radios support different functionality. The may be more or fewer options on this page, depending on the version of the radio.
Radio Network Settings
Use the settings in the Radio Network Settings panel to configure the radios in the network. For more information on using these settings, see Configuring the radios (Assign a Network name (SSID) of up to 32 characters. The radio uses this name in all network references. All radios in a network must have the same SSID. SSID names are case-sensitive.This control is only present on the RLX2-IHNF model. It allows the unit to be configured to operate in 802.11 a/g mode or to operate in 802.11n mode (default). In addition, it allows configuration of whether the unit will allow use of 40 MHz wide channels for Child clients. Note: The Parent radio link of a Repeater automatically uses a mode that is compatible with the Parent settings. For example, an RLX2-IHNF may connect to an RLX2-IHW master which only operates in 802.11a/g mode, and still use 802.11n mode for any Child Repeaters
The radio acts as an 802.11a radio on the 5 GHz band
and an 802.11g radio on the 2.4 GHz band. Data rates will be limited to the 802.11 a/g rates (54 mbps maximum). 802.11n operational features will be disabled. It is not necessary to select this mode for RLX2-IHNF radios to link to other RLX2 or RLXIB series radios; they will link their best possible speeds regardless of mode. This mode is not commonly used. It is mainly used to allow 802.11 a/b/g client devices that cannot link to 802.11n devices to work. One example of such a device is the ProSoft 1734-AENTR wireless I/O client. 802.11n Default operational mode of the RLX2-IHNF radio. All 802.11n features are operational, and 20 MHz wide channels are used.







Application industry
The products can be used in the following industries: power plant, paper making, steel, mining, rubber, water supply, cement, chemical industry, glass, printing Textile, machinery, plastics, coatings, medicine, hospitals, food, hotels, scientific research institutions