Home > Product > Robot control system > XYCOM XVME-210 Cylinder pressure monitor
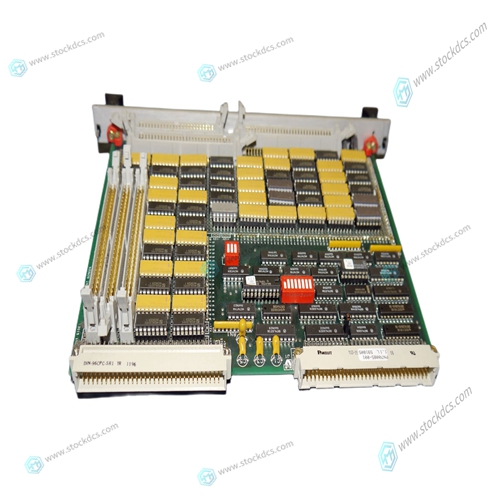
XYCOM XVME-210 Cylinder pressure monitor
- Product ID: XVME-210
- Brand: XYCOM
- Place of origin: The United States
- Goods status: new/used
- Delivery date: stock
- The quality assurance period: 365 days
- Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:+86 15270269218
- Email:stodcdcs@gmail.com
- Tags:XYCOMXVME-210Cylinder pressure monitor
- Get the latest price:Click to consult
XYCOM XVME-210 Cylinder pressure monitor
The G-64 bus idea was conceived at CERN in the late seventies around the Motorola 6809 microprocessor and was commercialised by GESPAC SA in 1979. It was quickly exploited as the computer bus for the power converter controls electronics in the CERN Proton-Synchrotron (PS) and Proton-Synchrotron Booster (PSB), and subsequently made its way into many other machines. Now, twenty-five years later, nearly 800 power converters at CERN are still controlled by electronics based on the G-64 bus and the MC6809 microprocessor running at just 4 MHz.
A key feature of any bus is the ability to divide functionality into separate cards.
This modularity enabled variants of the same design to be rapidly adapted to a very diverse population of power converters. This was particularly important as more and more commercial power converters were chosen to keep down costs, and each type came with a different interface, often lacking certain functionality such as remote control of converter state, reference, polarity inversion or precise timing. In the end, more than 20 variants of chassis were (and remain) in operation. This longevity is remarkable by any standard and justifies closer examination. How has it been possible to maintain and expand a system that belongs in a museum This paper examines the strengths and weaknesses of the original design, and looks at the lessons that may guide our technology choices today, as CERN embarks on an ambitious renovation program of its older machines.
Industrial bus standards have originated from a number of sources.
As semiconductor companies introduced new microprocessors, they also built a series of board and system products designed mainly to simplify their usage and accelerate the acceptance of their chips. These buses were often a direct extension of the microprocessor local bus onto a backplane. In fact, in the early days of the micro-computing industry, it was enough for a bus to ensure that boards plugged in the same backplane merely communicate. History includes a small number of bus architectures defined independently by other sources, for example, the S-100 bus from Altair or the G-64 bus from CERN/GESPAC. These buses have often done well in the market because they were aimed at specific needs and were relatively independent from any given chip or computer maker.




Quality assurance service
1. We provide high-quality parts of various brands, and you will find full
The model meets your needs.
2. For models that have been out of production for many years, we have all hard to find parts, so we can directly find us to solve all problems for you at one time.
3. If you are in a hurry to use this product, we can dispatch it for you.
4. All products can enjoy a one-year warranty service,
5. Our products are new and unused.
6. If you need a large quantity, you can contact us and I can offer you a discount.
7. You can ask me about the price and more information about the product via email. We welcome you