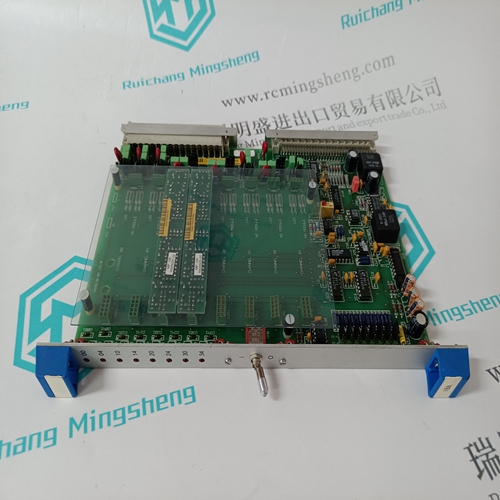
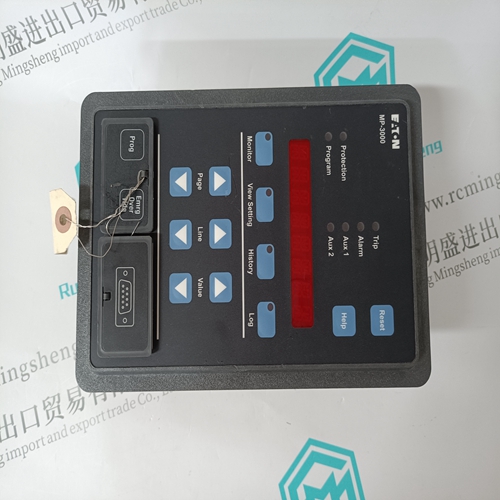
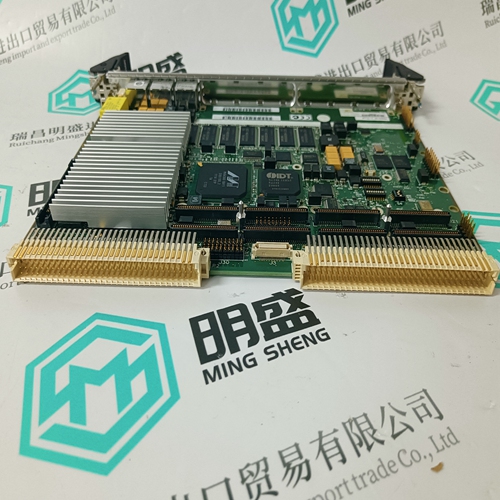
Home > Product > PLC programmable module > PROSOFT 4301-MBP-DFCM Bus gateway module
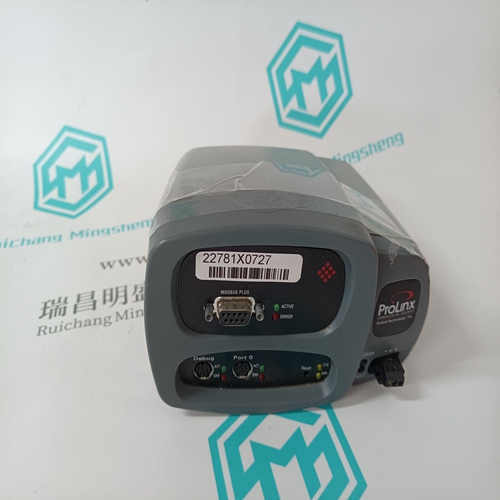
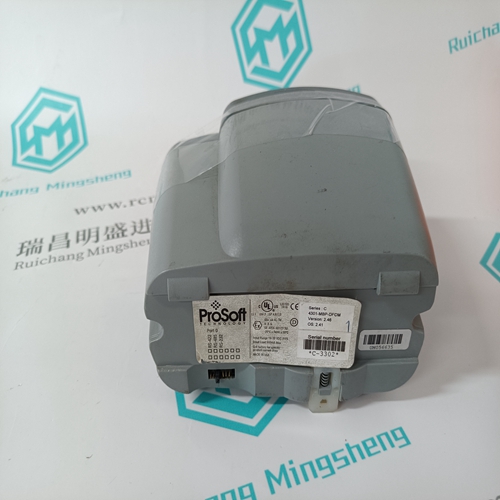
PROSOFT 4301-MBP-DFCM Bus gateway module
- Product ID: 4301-MBP-DFCM
- Brand: PROSOFT
- Place of origin: the United States
- Goods status: new/used
- Delivery date: stock
- The quality assurance period: 365 days
- Phone/WhatsApp/WeChat:+86 15270269218
- Email:stodcdcs@gmail.com
- Tags:PROSOFT 4301-MBP-DFCMBus gateway module
- Get the latest price:Click to consult
The main products
Spare parts spare parts, the DCS control system of PLC system and the robot system spare parts,
Brand advantage: Allen Bradley, BentlyNevada, ABB, Emerson Ovation, Honeywell DCS, Rockwell ICS Triplex, FOXBORO, Schneider PLC, GE Fanuc, Motorola, HIMA, TRICONEX, Prosoft etc. Various kinds of imported industrial parts
Products are widely used in metallurgy, petroleum, glass, aluminum manufacturing, petrochemical industry, coal mine, papermaking, printing, textile printing and dyeing, machinery, electronics, automobile manufacturing, tobacco, plastics machinery, electric power, water conservancy, water treatment/environmental protection, municipal engineering, boiler heating, energy, power transmission and distribution and so on.
PROSOFT 4301-MBP-DFCM Bus gateway module
The B885-002 ASCII / BASIC module runs user-written BASIC programs independently of the controller’s memory logic and scan. It also performs READ and WRITE commands to and from serial devices connected to either of the module’s two RS 232/422 ports (jumper selectable). In addition, its real-time clock/calendar allows the module to run a BASIC program or flag and return a value to the PLC at a user specified date and time. The module provides report generation, interactive operator interface, high level math, peripheral communication and data storage. Using a dumb terminal or an IBM personal computer with Emulator Software (Part # SW-E885-1DA), you program the module’s 53K of user memory. If you need more memory, you may provide an additional 32K of user EPROM. You can designate part of the memory as retentive variable memory to store formulas or other process parameters
User connections are made to a standard screw terminal strip.The rigid wiring system permits module insertion or removal without disturbing the wiring. Terminal Numbering and Output Connections The following diagram shows terminal numbering and output connections for the the B885-002 module.
Module B885-1xx, Motion Modules
B885-1xx motion modules are high performance, single axis servo motion controllers contained in a single-width 800-Series I/O module. They are designed to plug directly into the I/O rack of the 984 PLC, although they are capable of standalone operation. The modules use Schneider Automation's patented Direct Numerical Processing (DNP) technology. Advanced digital brushless motion control eliminates potentiometer adjustments and analog velocity loops for optimal control. The B885-100 / B885-101 module uses a resolver to provide feedback for the position, velocity, and commutation of the motor. Essentially, a rotary brushless transformer that provides absolute position information to the motion module, the resolver gives the module a high degree of noise immunity. The B885-110 / B885-111 module additionally has two quadrature encoder interfaces for extra position and velocity feedback. Control communication interface to the B885-1xx modules can be either through the 800 I/O system backplane or the Modbus/RS-232 serial port. The module is designed to work directly with the Cyberline 1000 series brushless servo amplifiers as well as those of third-party vendors. The PLC communicates with the motion modules through six input and six output registers with the control instructions providing a powerful, smooth and fast link between the two. Adjustable command buffering and direct register to function bits provide added communication speed for high response functions. Motion programs, developed using MMDS, are either stored directly in the flash memory of the motion module or as registers in the PLC. The Motion Development Software (MMDS) is an on-line/ off-line, menu driven package (Part # SW-MMDS1DB) for the IBM-AT or compatible computers. It enables the user to set up, program, operate and diagnose operation of the motion module. The program and file manipulation features are a versatile system for application management. The MMDS communicates via a computer serial port to the Modbus port on the motion module.
800 Series I/O Modules with Unity Addressing Modes
To allow an easy transition from the register addressing (3x, 4x) of 984LL to the IEC addressing modes used in Unity Pro, this chapter describes z Flat Addressing z Topological Addressing NOTE: Topological addresses overlapping (%IWr.m.c) is not supported by Quantum application, use flat addressing (%IWx) when memory overlapping control is needed.
The following example compares the 2 possible addressing modes. An 8-channel analog input module B875-200 with the following configuration data is used: z mounted in slot 5 of the RIO rack #3 located at drop 4 on bus 2 z starting input address is 201 (input word %IW201) z end input address is 208 (input word %IW208)
The following example compares the 2 possible addressing modes. An 32-channel discrete output module B838-032 with the following configuration data is used: z mounted in slot 4 of the RIO rack #3 located at drop 4 on bus 2 z starting output address is 101 (output word %MW101) z end output address is 102 (output word %MW102)